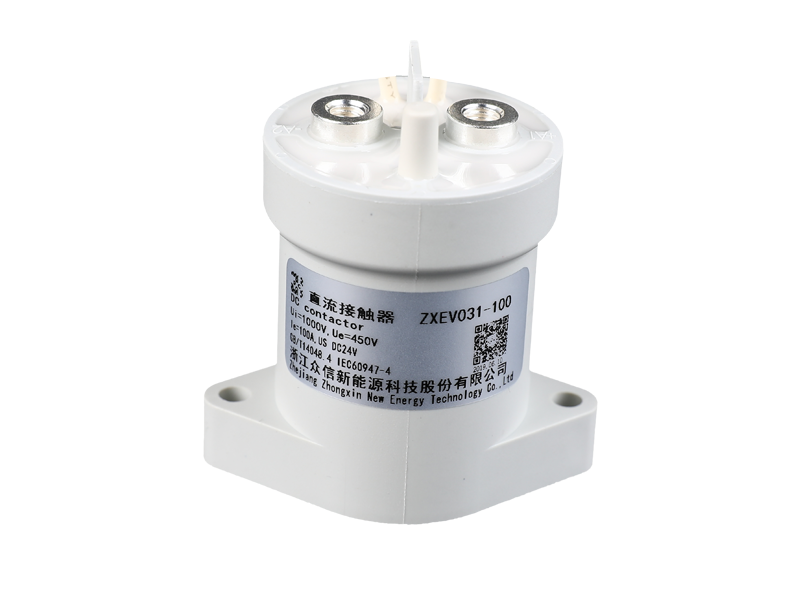
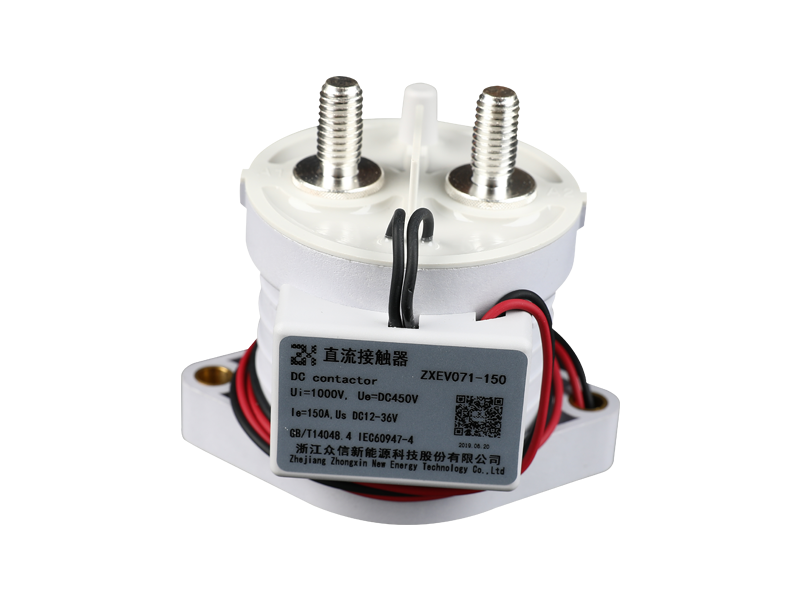
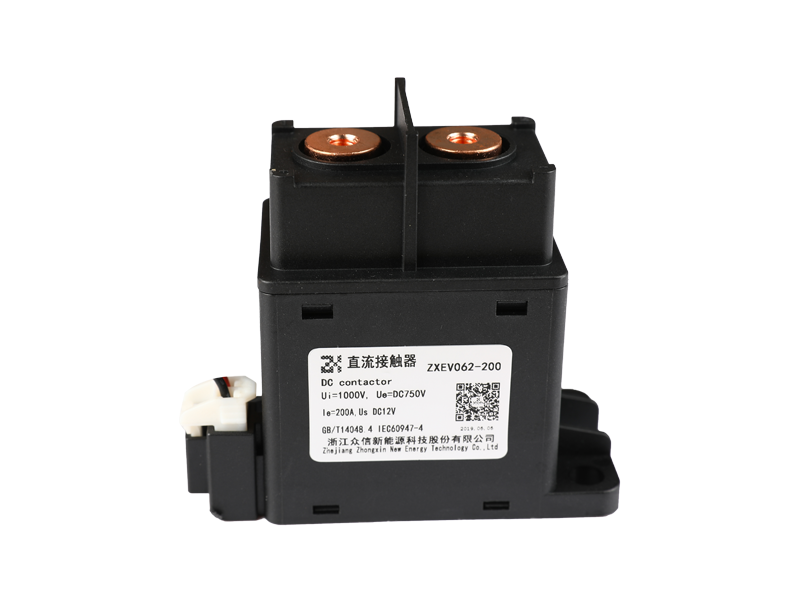
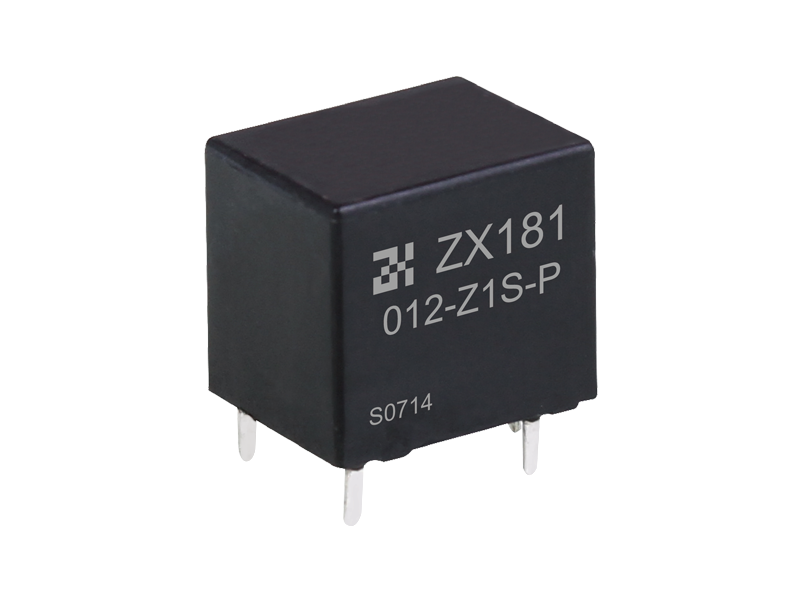
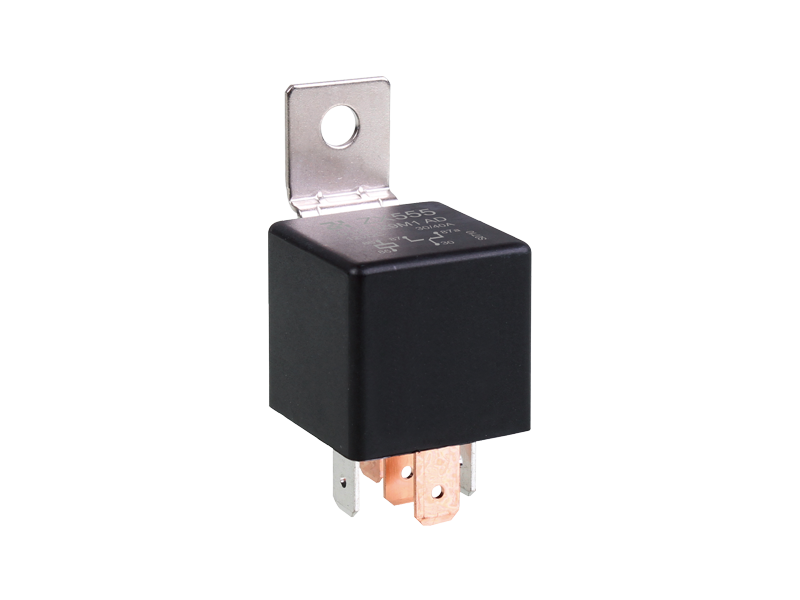
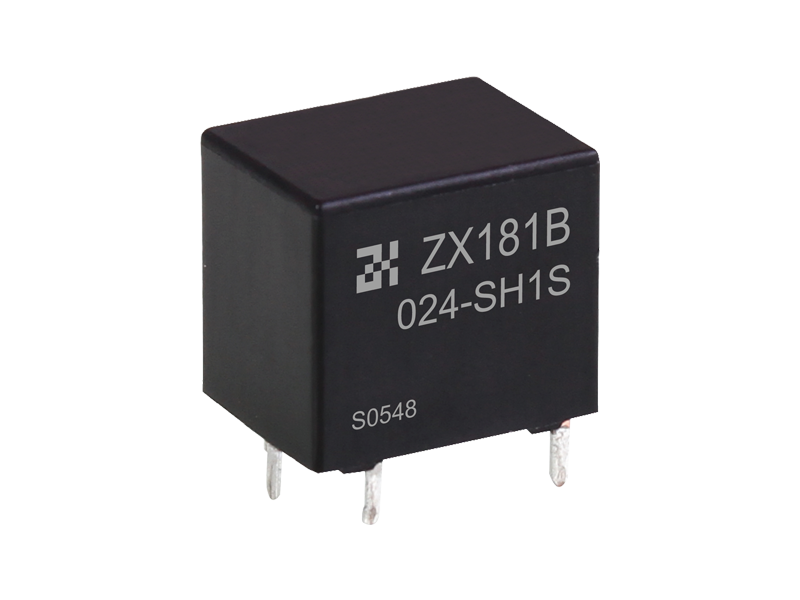
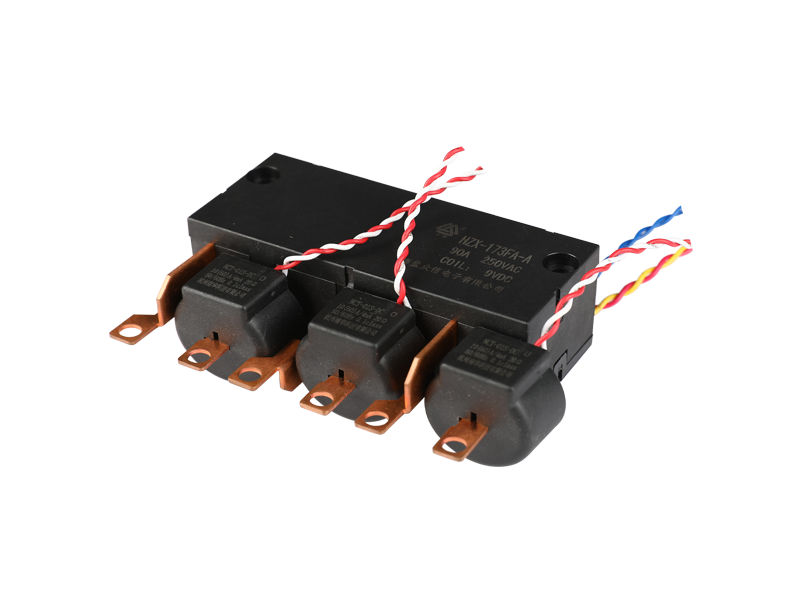
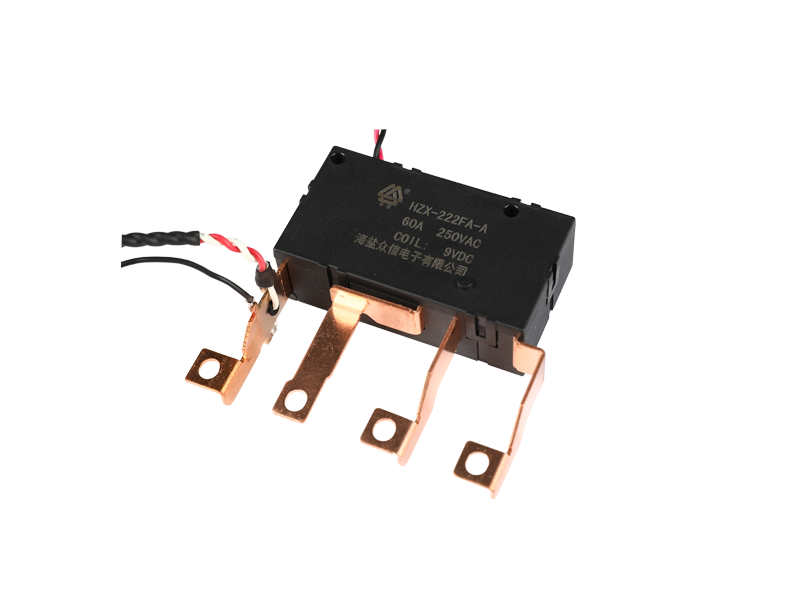
The basic function of the automotive relay is to use a small current to control the operation of a large current, as an "automatic switch". It plays the role of automatic adjustment, safety protection, switching circuit and switch in the circuit. If a car relay is bad, the simplest symptom is that some function of the car cannot be used. If the oil pump relay is broken, the engine will not start. If the headlight relay is broken, the headlights won't come on. If the starter relay is broken, the car will not start. There are normally closed contacts, normally open contacts and two coil contacts inside the relay. Generally, there are signs on the shell. Normally closed becomes normally open and normally open becomes normally closed when the coil is energized. The most useful and common is the turn signal on the car. Or turn on the power of the control circuit, such as the alarm device. Judging whether the relay is good or bad; 1. Turn on the ignition switch, then listen with your ears or a stethoscope to see if there is any suction sound in the control relay, or feel the vibration of the relay with your hands. If there is, it means that the relay basically works normally, and the electrical failure is caused by other reasons; otherwise, the relay will fail. Common failures of automotive relays include: coil burnout, inter-turn short circuit, contact ablation, thermal decay, and inability to adjust the initial operating current. 2. Use a digital multimeter with a resistance of 2k to measure the resistance of the coil. The relay models are different, the voltage is different, and the resistance value is different. Generally it will be within 2k. 3. The relay has a normally open point, a normally closed point and a common terminal. When no power is applied, measure the resistance between the normally closed point and the common terminal with a digital multimeter. This resistance is very small and can be approximately zero. 4. In the case of no power, use a digital multimeter to measure the resistance between the normally open point and the common terminal, and the resistance is very large. 5. Apply working voltage to the relay coil, and measure the resistance between the normally open point and the common terminal with a digital multimeter. This resistance is very small and can be approximately zero. 6. Apply working voltage to the relay coil, and use a digital multimeter to measure the resistance between the normally closed point and the common terminal. This resistance is very high. If your measurements are as above, then the relay can be assumed to be working fine.