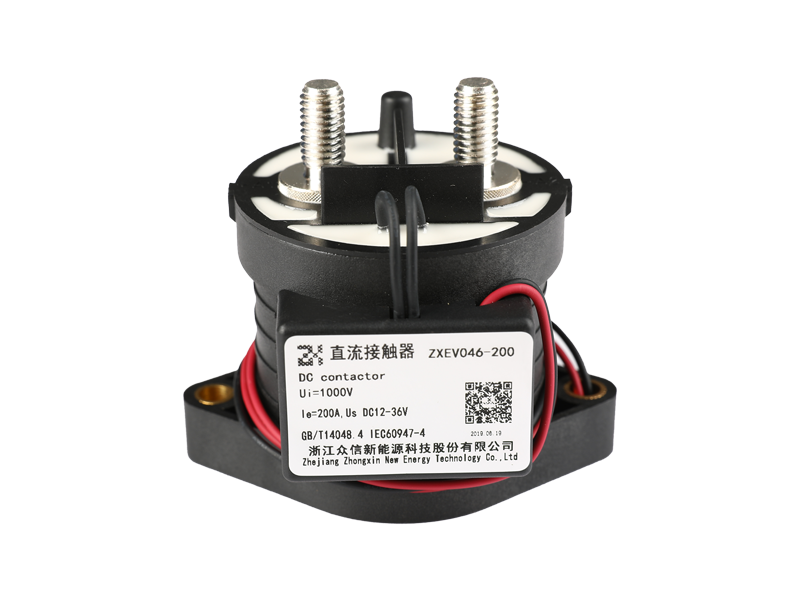
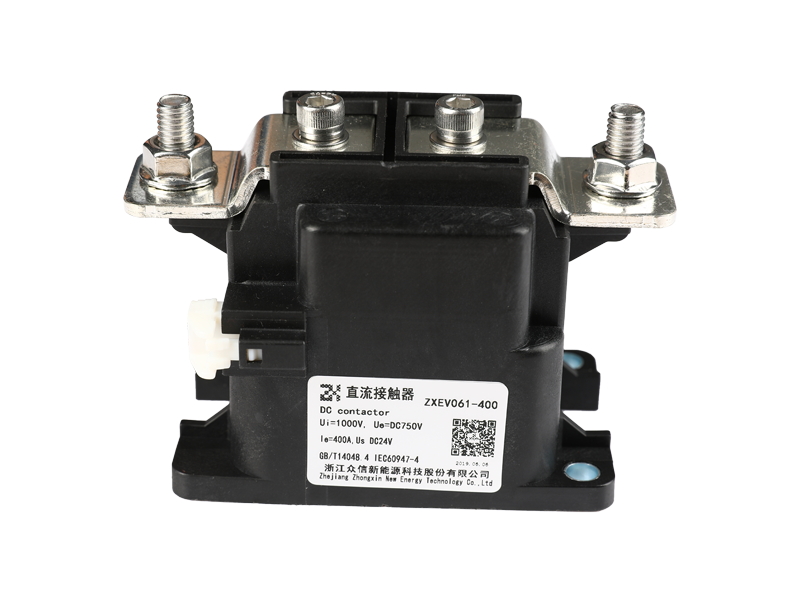
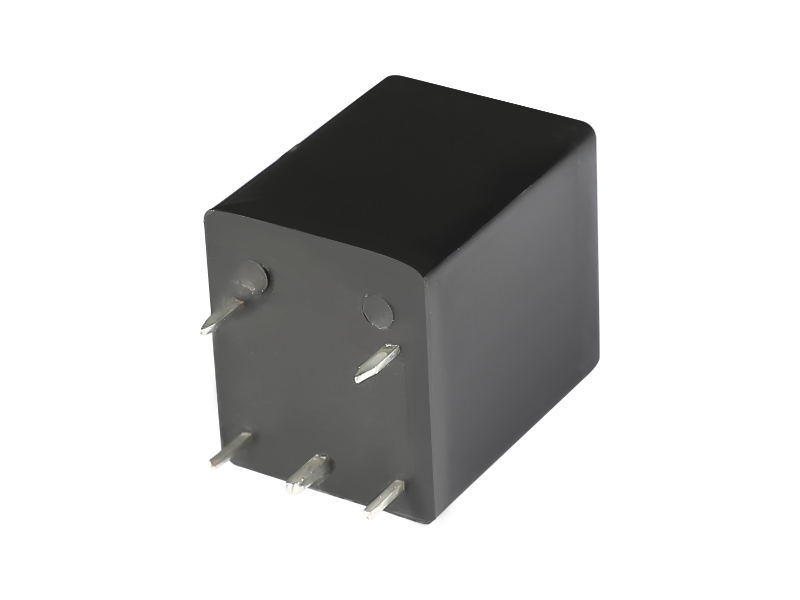
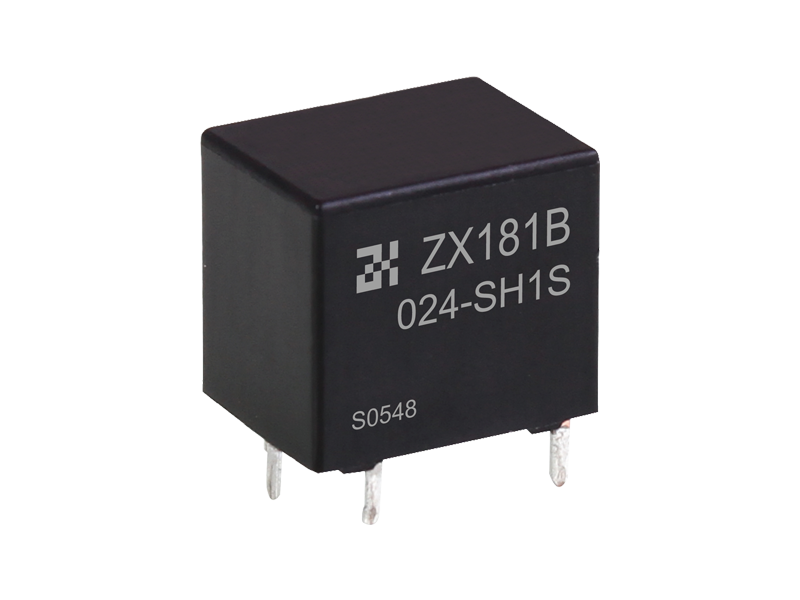
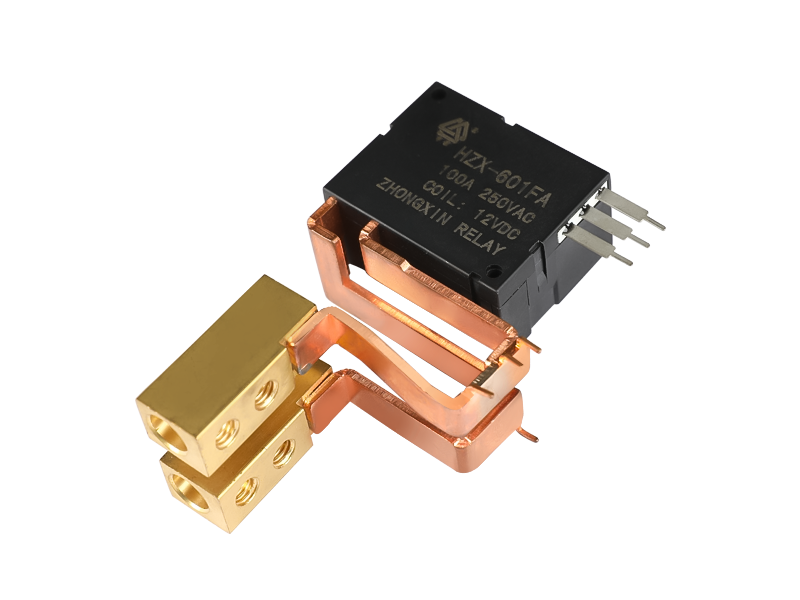
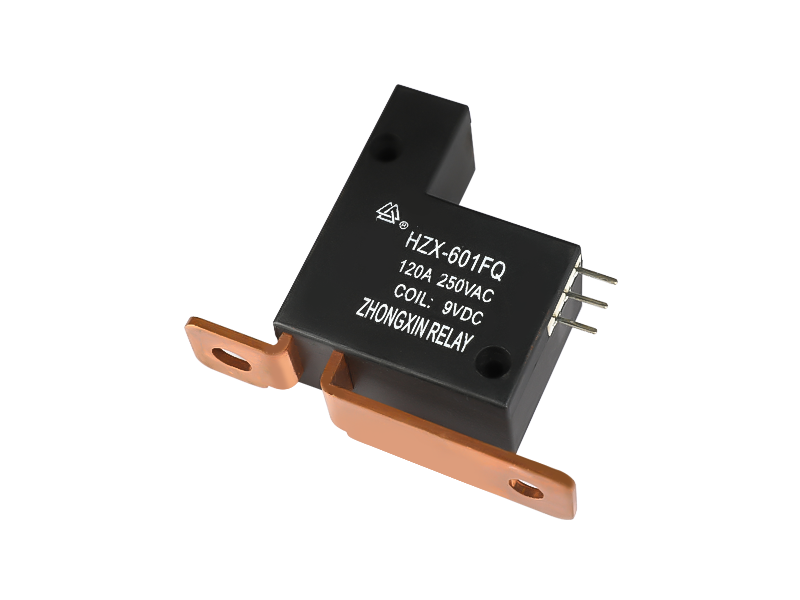
Voltage relay is a commonly used electromagnetic relay, and voltage relay is used for voltage protection and control of power drag system. The coil is connected to the main circuit in parallel to sense the line voltage of the main circuit; the contact is connected to the control circuit and is the executive element.
According to the size of the pull-in voltage, voltage relays can be divided into over-voltage relays and under-voltage relays. The overvoltage relay (FV) is used for the overvoltage protection of the line, and its pull-in setting value is 1.05 to 1.2 times the rated power of the protected line. When the voltage of the protected line is normal, the armature does not act; when the voltage of the protected line is higher than the rated value and reaches the set value of the overvoltage relay, the armature pulls in, the contact mechanism acts, the control circuit loses power, and the contactor is controlled Disconnect the protected circuit in time. The under-voltage relay (VK) is used for under-voltage protection of the line, and its release setting value is 0.1 to 0.6 times the rated voltage of the line. When the voltage of the protected line is normal, the armature pulls in reliably; when the voltage of the protected line drops to the release setting value of the Undervoltage relay, the armature is released, the contact mechanism is reset, and the contactor is controlled to break the protected circuit in time. The zero-voltage relay is released when the circuit voltage drops to 5% to 25% UN, and realizes zero-voltage protection for the circuit. Voltage loss protection for lines. The intermediate relay is essentially a voltage relay. Its characteristic is that the number of contacts is large, the current capacity can be increased, and it plays the role of intermediate amplification (the number of contacts and current capacity).