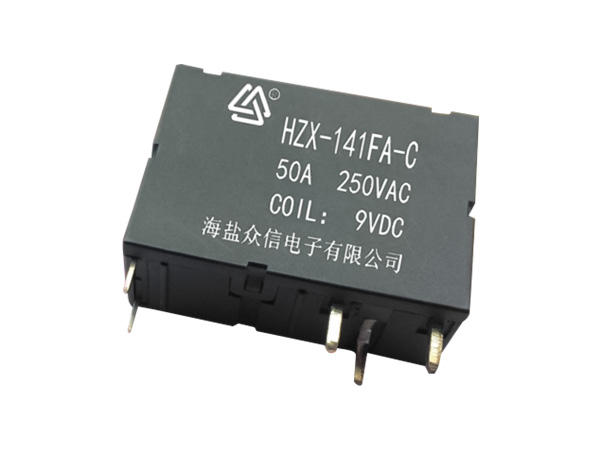
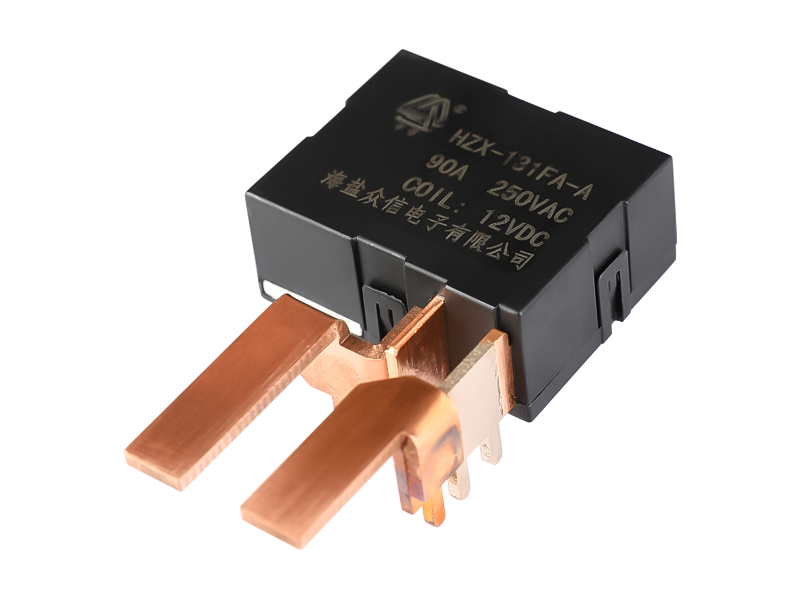
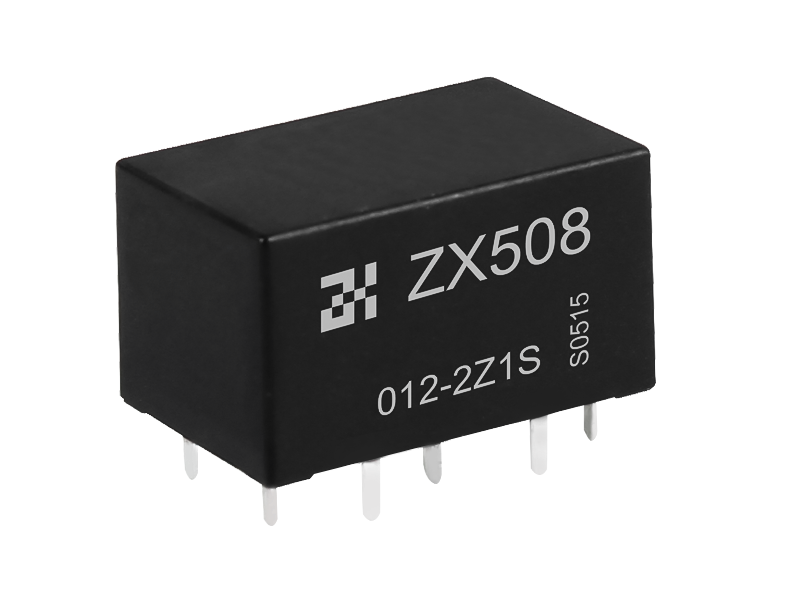
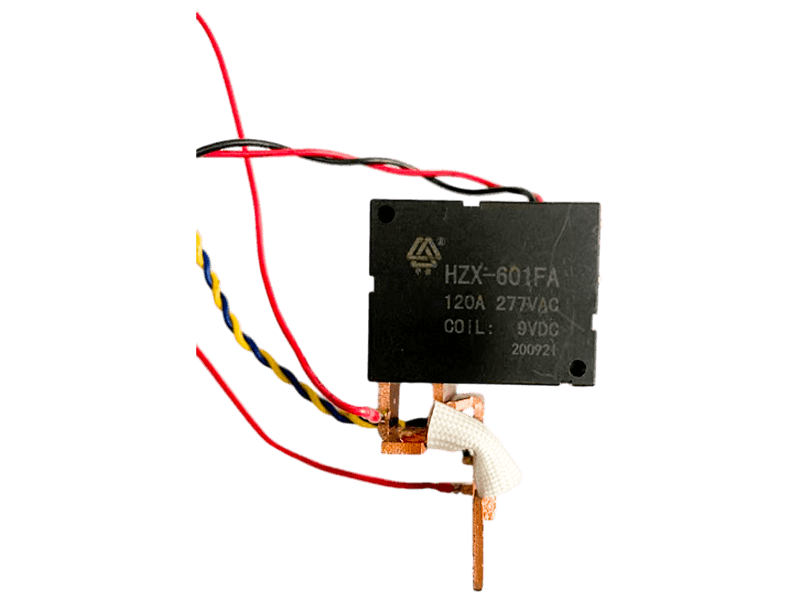
Intermediate relays are used in relay protection and automatic control systems to increase the number and capacity of contacts. They are also used to transmit intermediate signals in control circuits. The structure and principle of the intermediate relay are basically the same as the AC contactor. The main difference from the contactor is that the main contact of the contactor can pass a high current, while the contact of the intermediate relay can only pass a small current, so it can only be used In the control circuit, which generally does not have the main contact. Because the overload capacity is relatively small, all it uses are auxiliary contacts, and the number is relatively large. The definition of the new national standard for the intermediate relay is K, which is generally DC power supply, and a few use AC power supply.
The intermediate relay has the same principle as the AC contact, which is composed of a fixed iron core, a moving iron core, a spring, a moving contact, a static contact, a coil, a terminal, and a shell. When the coil is energized, the moving iron core acts to pull in under the action of the electromagnetic force, driving the moving contacts to move, so that the normally closed contacts are separated and the normally open contacts are closed; the coil is de-energized, and the moving iron core drives the moving contacts under the action of the spring Reset.
There are two main delay modes of the intermediate relay, namely the power-on delay and the power-off delay. The installation methods are mainly divided into fixed, protruding, embedded, and guide rail types. It generally does not have the main contact, because the overload capacity is relatively small. So all it uses are auxiliary contacts, and the number is relatively large.
There are many types of intermediate relays. According to the structure, there are electromagnetic relays and static relays:
1. Static intermediate relay:
The static integrated circuit type intermediate relay adopts the principle structure of the integrated circuit and has good anti-vibration. It is suitable for various power relay protection and automatic control devices to increase the contact capacity and the number of contacts for protecting and controlling the hoist. The static intermediate relay is composed of electronic components and precision small relays, etc., and is the first choice for the renewal of power series intermediate relays.
1) The static intermediate relay is more precise in use, moisture-proof, dust-proof, uninterrupted, and has high reliability. It overcomes the shortcomings of the electromagnetic intermediate relay that the wire is too thin and easy to break.
2) Low power consumption, low-temperature rise, no need for external high-power resistors, easy to install and connect at will.
3) Large relay contact capacity and long working life.
4) After the relay is activated, there is a light-emitting tube indicator, which is convenient for on-site observation.
5) High insulation withstand voltage level. The contact capacity is large, and the contact resistance is small.
2. Electromagnetic intermediate relay
The electromagnetic intermediate relay is a traditional old-fashioned relay. As long as a certain voltage is applied to both ends of the coil, a certain current will flow through the coil, which will produce electromagnetic effects. The armature will overcome the return spring under the action of electromagnetic force. The pulling force is attracted to the iron core, thereby driving the movable contact and the static contact of the armature to attract. When the coil is de-energized, the electromagnetic attraction will also disappear, and the armature will return to its original position under the reaction force of the spring, releasing the moving contact and the original static contact. This pulls in and releases, so as to achieve the purpose of conducting and cutting off in the circuit.