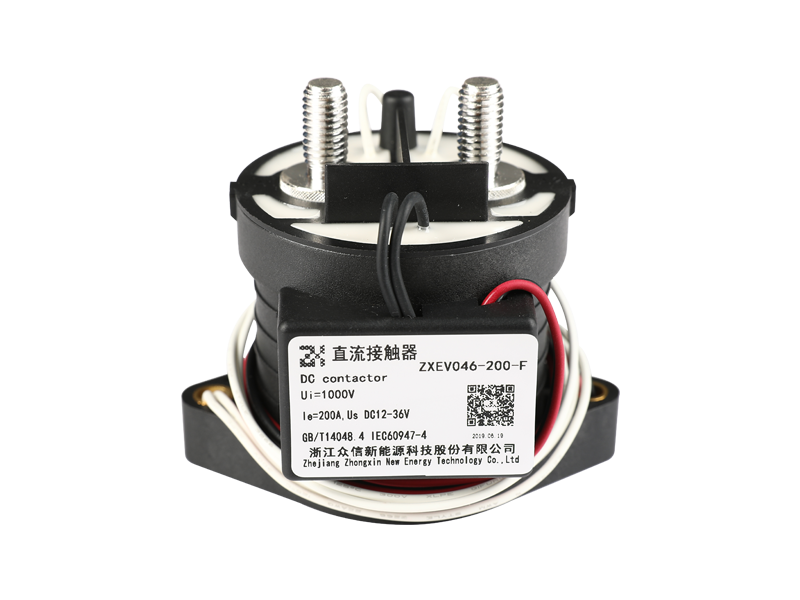
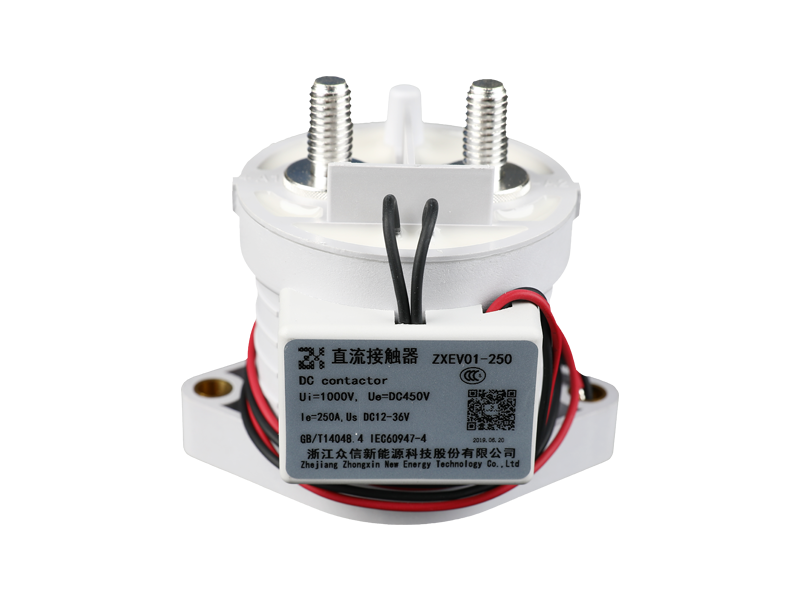
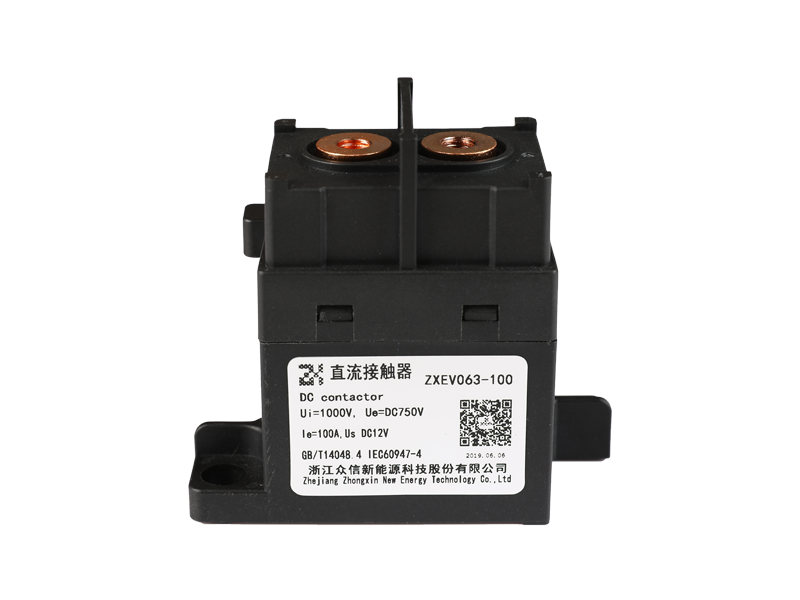
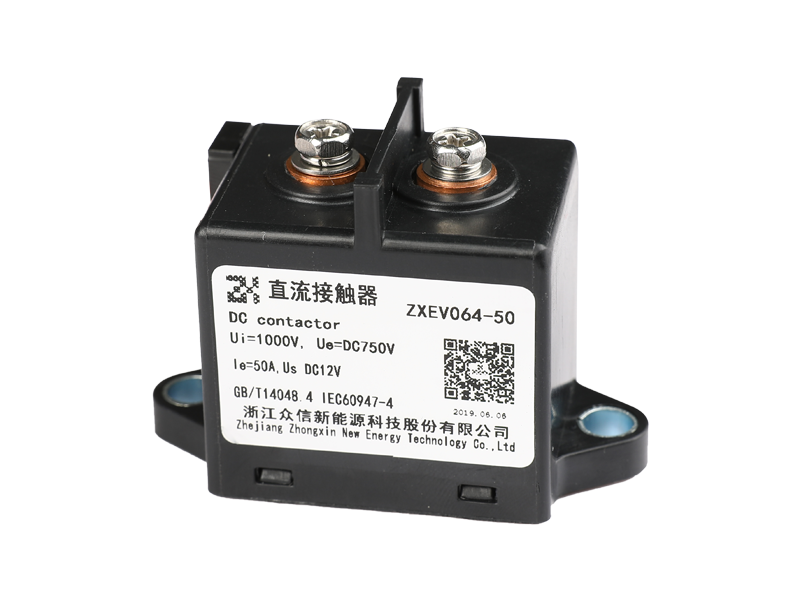
The difference between the current relay and the voltage relay in structure.
Mainly the coils are different.
The coil of the current relay is connected in series with the load to reflect the load current, so the number of coil turns is small and the wire is thick, so that the voltage drop when passing the current is small and will not affect the current of the load circuit. The coil of the voltage relay is connected in parallel with the load to reflect the load voltage, and the coil has many turns and thin wires.
What is the difference between current type signal relays and voltage type signal relays? How do distinguish them in use?
Current type signal relay;
Low voltage, large current, thick wire, a small number of turns, small impedance, small size, generally used in series with electrical appliances.
Voltage type signal relay;
The voltage is high, the current is small, the wire is thin, the number of turns is large, the impedance is large, and the volume is large. Generally, it is directly connected to both ends of the power supply through a switch.
Characteristics and applications of voltage relays and current relays.
A voltage relay is a commonly used electromagnetic relay, voltage relay is used for voltage protection and control of the power drag system.
The coil of the voltage relay is connected to the main circuit in parallel to sense the line voltage of the main circuit; the contact is connected to the control circuit and is the executive element.
According to the size of the pull-in voltage, voltage relays can be divided into over-voltage relays and under-voltage relays.
The overvoltage relay (FV) is used for overvoltage protection of the line, and its pull-in setting value is 1.05 to 1.2 times the rated power of the protected line. When the voltage of the protected line is normal, the armature does not act; when the voltage of the protected line is higher than the rated value and reaches the set value of the overvoltage relay, the armature pulls in, the contact mechanism acts, the control circuit loses power, and the contactor is controlled Disconnect the protected circuit in time.
The under-voltage relay (VK) is used for under-voltage protection of the line, and its release setting value is 0.1 to 0.6 times the rated voltage of the line. When the voltage of the protected line is normal, the armature pulls in reliably; when the voltage of the protected line drops to the release setting value of the Undervoltage relay, the armature is released, the contact mechanism is reset, and the contactor is controlled to break the protected circuit in time. The zero-voltage relay is released when the circuit voltage drops to 5% to 25% UN to achieve zero-voltage protection for the circuit. Voltage loss protection for lines.
Supplementary skills: The intermediate relay is essentially a voltage relay. Its characteristic is that the number of contacts is large, the current capacity can be increased, and it plays the role of intermediate amplification (the number of contacts and current capacity).
(2) Characteristics and applications of current relays.
The current relay is a commonly used electromagnetic relay, and the current relay is used for the current protection and control of the power drag system. The coil is connected to the main circuit in series to sense the line current of the main circuit; the contact is connected to the control circuit and is the executive element.
The current relay reflects the current signal. Commonly used current relays are undercurrent relays and overcurrent relays.
The undercurrent relay (KA) is used for circuit undercurrent protection. The attracting current is 30% to 65% of the rated current of the coil, and the release current is 10% to 20% of the rated current. Therefore, when the circuit is working normally, the armature is pulled in. , only when the current drops to a certain set value, the relay is released, and the control circuit loses power, thereby controlling the contactor to break the circuit in time.
The overcurrent relay (FA) does not act when the circuit is working normally, and the setting range is usually 1.1 to 4 times the rated current. When the current of the protected circuit is higher than the rated value and reaches the setting value of the overcurrent relay, the armature pulls in and touches The point mechanism moves, and the control circuit loses power, thereby controlling the contactor to break the circuit in time. Overcurrent protection for the circuit.