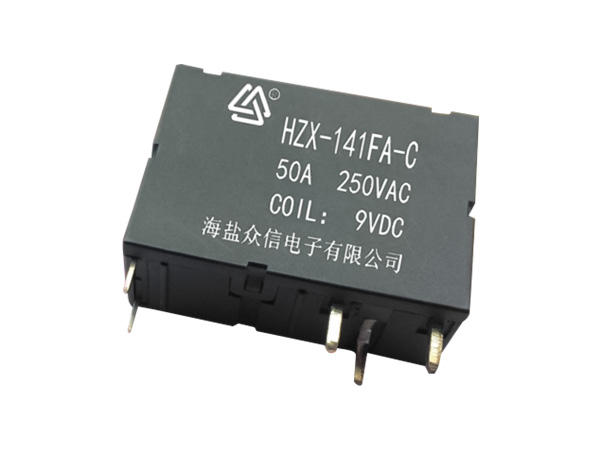
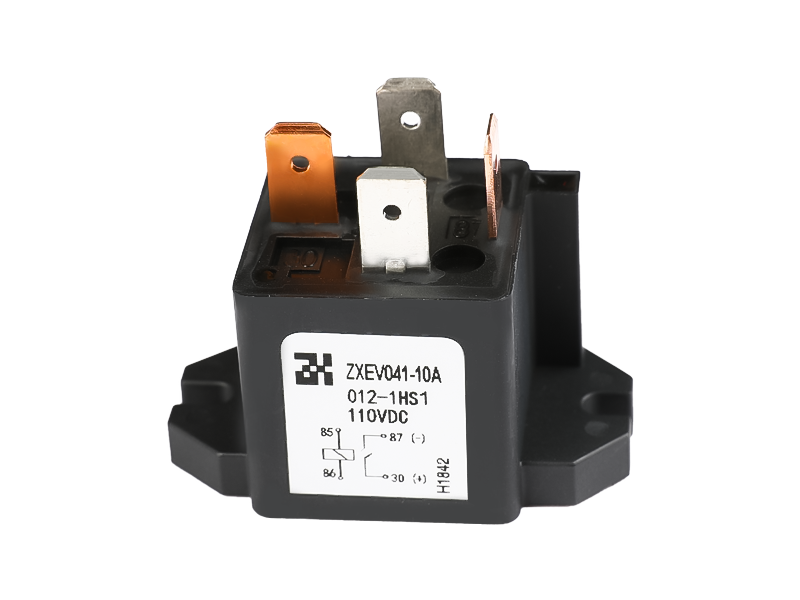
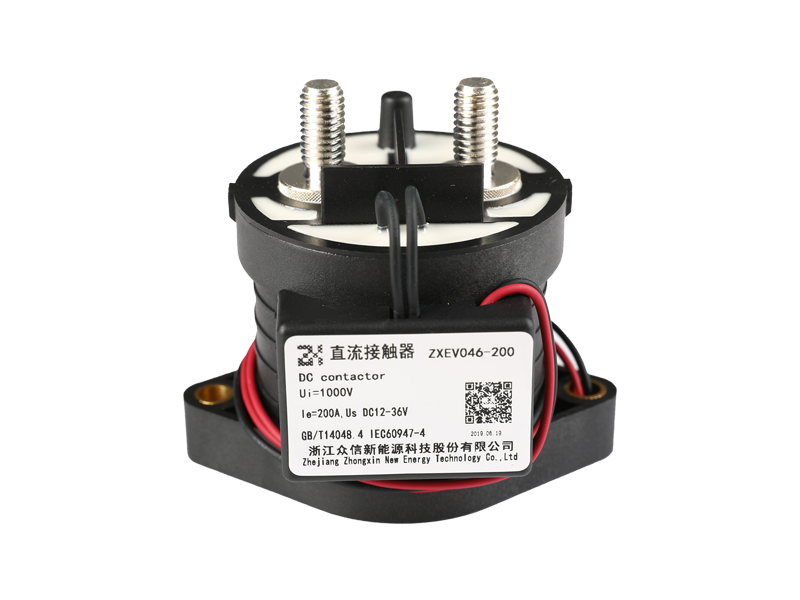
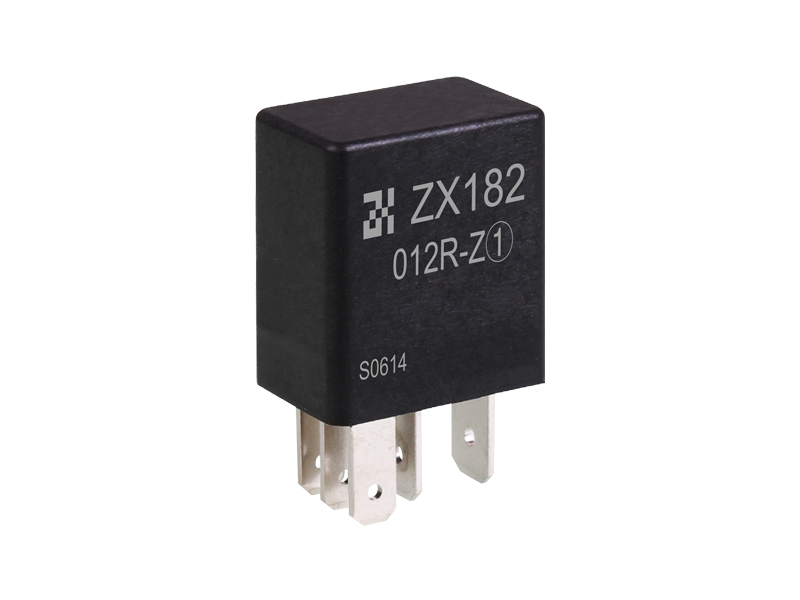
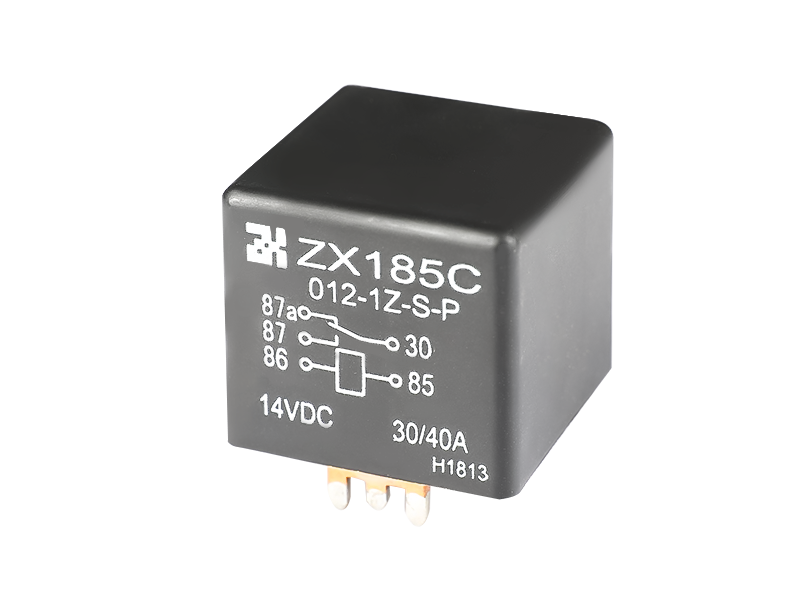
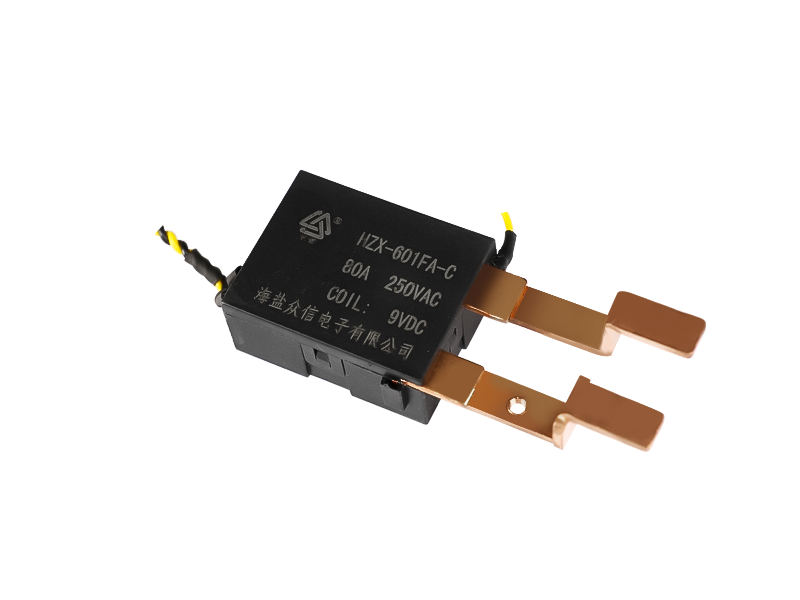
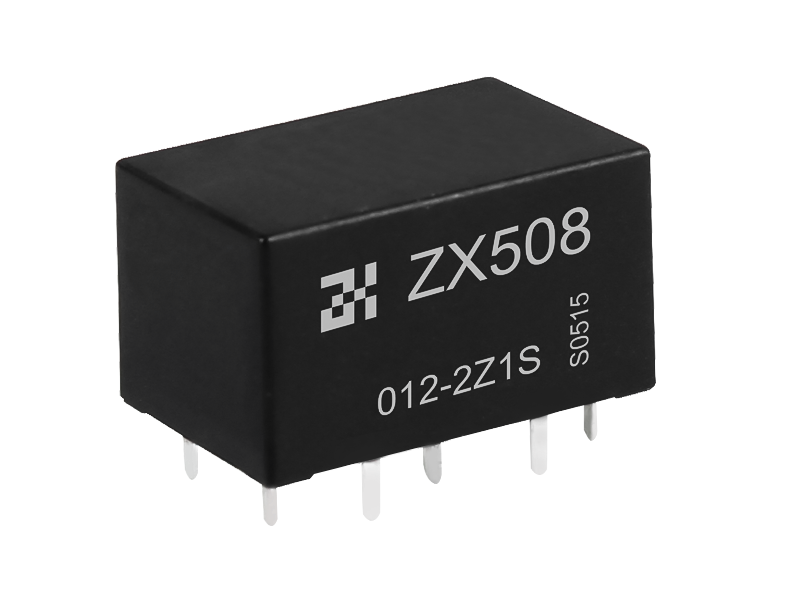
If the electromagnetic relay works in simple words, when the electromagnet is energized, the armature is sucked down to make the two contacts and the working circuit is closed. The electromagnet loses its magnetism when it is powered off, and the spring pulls up the armature to cut off the working circuit. It is usually used in automatic control circuits. It is actually an "automatic switch" that uses a smaller current to control a larger current. Therefore, it plays the role of automatic adjustment, safety protection and conversion circuit in the circuit. It can be seen from the function that it has at least two major parts, the control system (also known as the input loop) and the controlled system (also known as the output loop). The former is the most important part of the main electromagnetic relay that needs to be understood. If it is divided, it can be divided into three parts: electromagnetic system, contact system, transmission and recovery mechanism.

Now that you know the three core parts of the electromagnetic relay (electromagnetic system, contact system, transmission and recovery mechanism), how do they work?
1. Electromagnetic system: the induction mechanism, which is composed of a magnetic circuit system and a coil composed of an iron core, a yoke and an armature made of soft magnetic materials. Power is magnetic, which is the core part of electromagnetic relay;
2. Contact system: the actuator, which is assembled from different forms of contact springs or contact sheets used as contacts with a certain insulation. The part that determines which circuit is energized;
3. Transmission and recovery mechanism: the intermediate comparison mechanism, the transmission mechanism that realizes the relay action refers to the mechanism that transmits the armature movement to the contact spring when the coil is excited. Generally, the contact reed connected with the armature is directly driven or indirectly pushed through the movement of the armature.